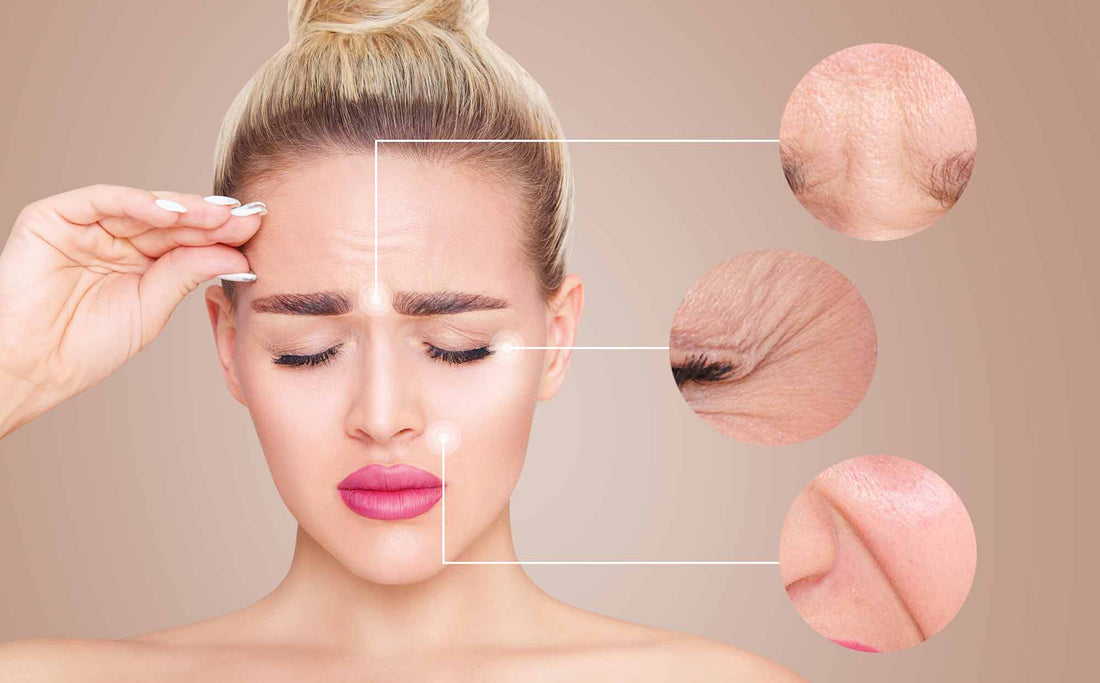
Collagen is the protein that holds our bodies together - from skin to bones. It is the “glue” that provides strength, elasticity and tissue regeneration. But over time, our natural production decreases, leading to the typical signs of aging. In this post, we'll look at what collagen really is, how it affects our bodies, and what we can do to maximize its benefits.
What is collagen good for?
Collagen is an essential protein and a fundamental building block of our body, present everywhere - from the skin to bones and joints. It forms the basic structure of our skin, provides strength and elasticity and plays a central role in the healing and regeneration of tissue.
There are different types of collagen, each with specific functions in different parts of the body. Maintaining and promoting collagen production is crucial to the health of our skin and joints and helps delay the signs of aging.
Collagen types
There are at least 16 different types of collagen, but most structures in the body are made up of types I, II, III, IV, and V.
Each type has special features:
- Type I is found particularly in skin , tendons, organs and bones;
- Type II is present in cartilage and eyes;
- Type III supports the structure of muscles, organs and arteries;
- Types IV and V are found in cell layers.
Knowing these types helps us understand how collagen works in our body and what role it plays in our health.
Collagen effect
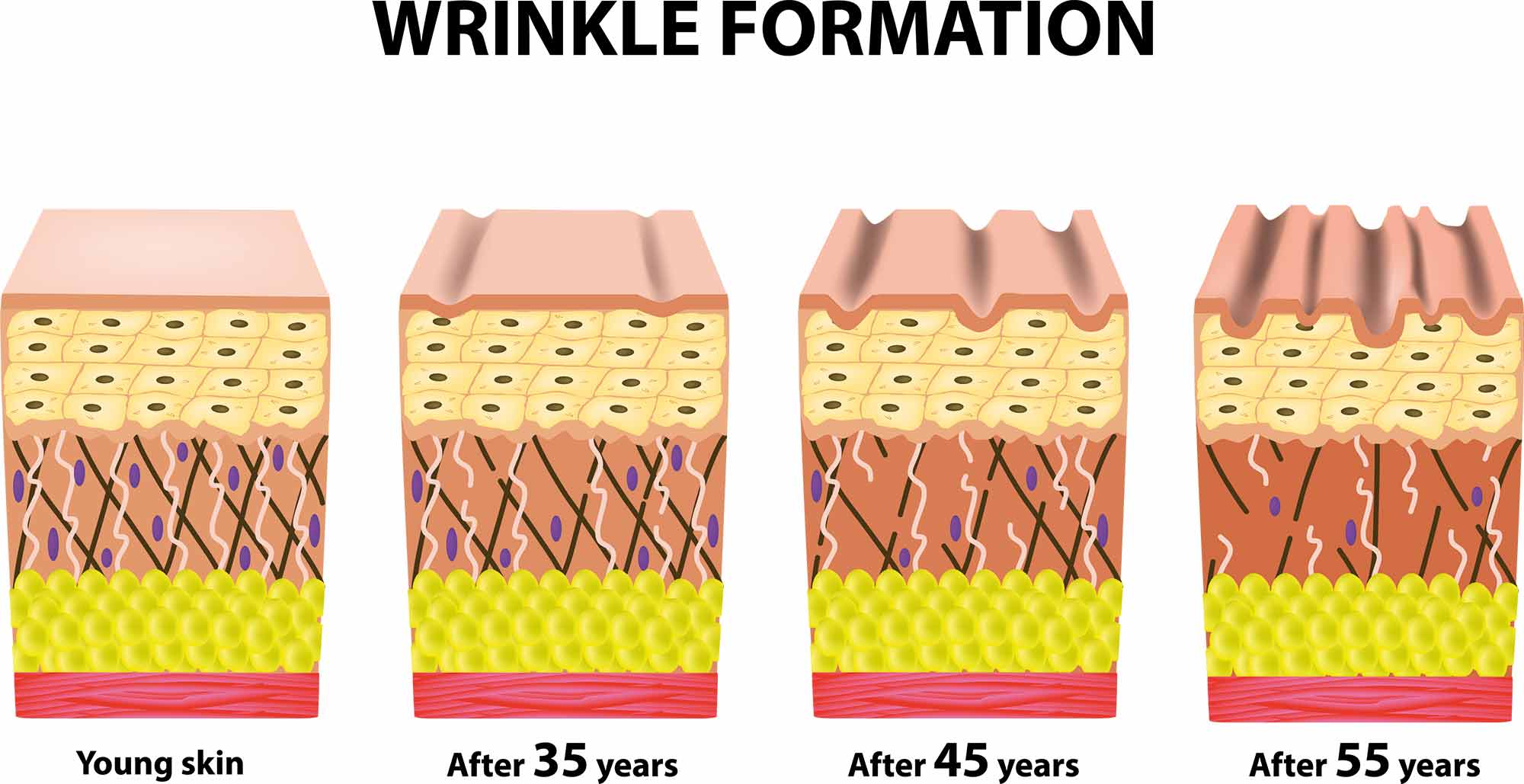
Collagen has diverse and significant effects on our body. It is crucial for maintaining healthy, elastic skin and helps reduce wrinkles and dry skin. In the joint area, collagen supports elasticity and mobility and can help relieve joint pain. In addition, it plays an important role in maintaining the health of hair and nails by giving them strength and vitality.
So maintaining high collagen levels is essential for overall physical health and well-being.
How does natural collagen production work?
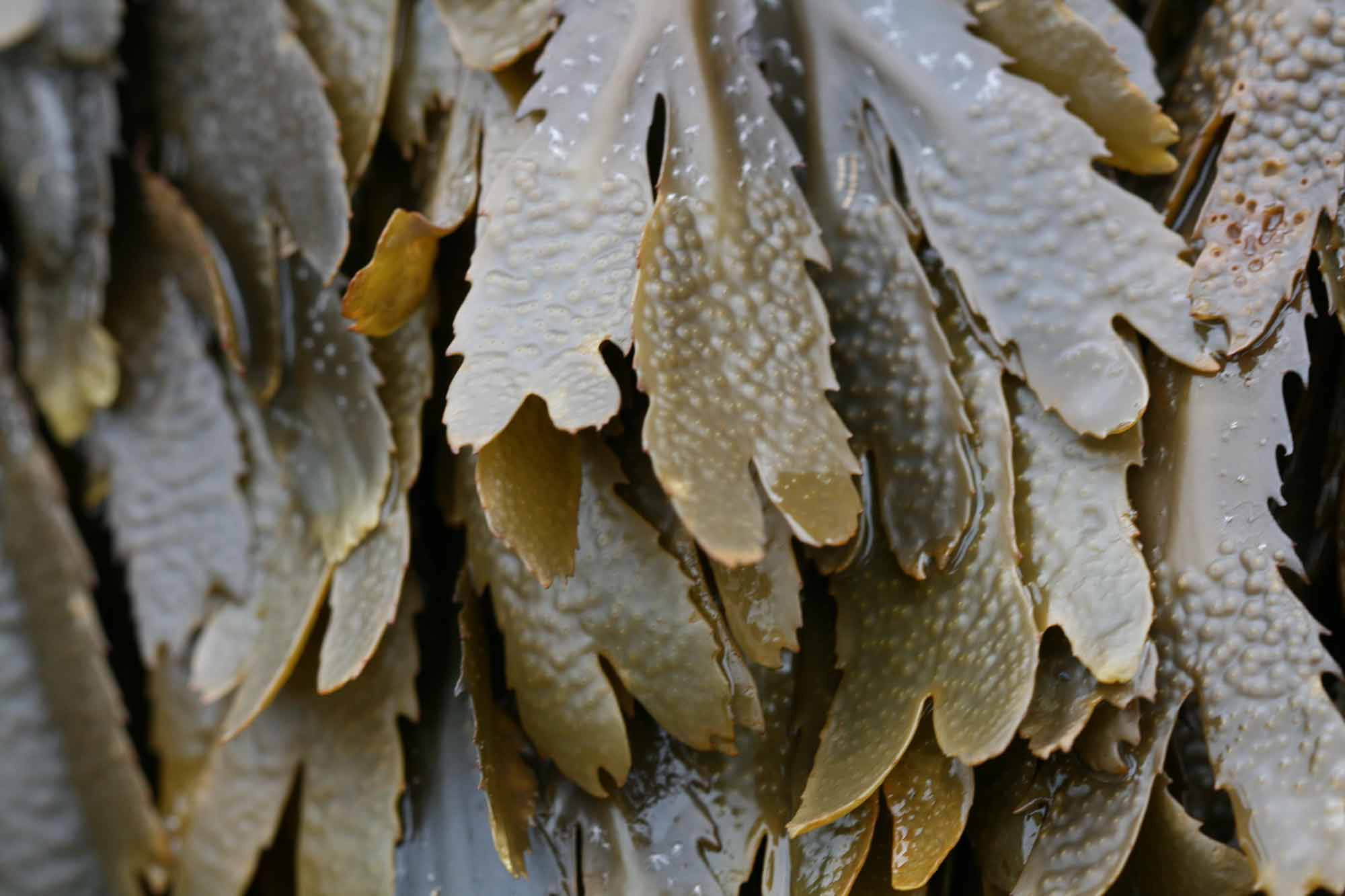
The role of nutrition in natural collagen production is crucial. Specific “collagen foods,” such as seaweed, are rich in nutrients that support collagen synthesis. Algae such as Fucus serratus contain important elements such as fucoidan and antioxidants that contribute to collagen formation. In addition to algae, other foods such as citrus fruits and green leafy vegetables can also provide the necessary vitamins and minerals for collagen production.
Nutrition and collagen
A special feature of Fucus serratus is the high content of fucoidan, a substance found in brown algae and known for its health-promoting properties. Fucoidan supports collagen production and helps to improve skin structure and increase its elasticity. This also has a positive effect on skin regeneration. The combination of fucoidan with other nutrient-rich ingredients in Fucus serratus makes this seaweed a valuable addition to a diet aimed at supporting natural collagen synthesis.
Myths and misconceptions
There are some misunderstandings when it comes to collagen, especially regarding the effect of dietary supplements such as collagen powder or collagen capsules.
Although supplemental collagen is popular, it is broken down into amino acids in the body with no guarantee of effective collagen synthesis. This makes it less targeted compared to promoting natural collagen production through a nutrient-dense diet. Foods rich in collagen-supporting nutrients are a more effective method because they directly support the body's ability to produce collagen.
This holistic approach, which supports the body's own collagen production through a nutrient-rich diet, is simply more effective.
Additionally, brown seaweed fucoidan provides antioxidant and anti-inflammatory benefits that promote skin and joint health, forming a comprehensive approach to supporting skin health.

Current research and studies
The latest research highlights the importance of collagen peptides for skin health. Studies show that collagen peptides can improve skin elasticity, resulting in a reduction in wrinkles and fine lines. There is also evidence that they support the healing process of wounds. These findings confirm that increasing collagen production in the body offers a variety of health benefits, from improved skin texture to more effective wound healing.

